|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
# nsenter -h 用法: nsenter [options] <program> [<argument>...] Run a program with namespaces of other processes. 选项: -t, --target <pid> 要获取名字空间的目标进程 -m, --mount[=<file>] enter mount namespace -u, --uts[=<file>] enter UTS namespace (hostname etc) -i, --ipc[=<file>] enter System V IPC namespace -n, --net[=<file>] enter network namespace -p, --pid[=<file>] enter pid namespace -U, --user[=<file>] enter user namespace -S, --setuid <uid> set uid in entered namespace -G, --setgid <gid> set gid in entered namespace --preserve-credentials do not touch uids or gids -r, --root[=<dir>] set the root directory -w, --wd[=<dir>] set the working directory -F, --no-fork 执行 <程序> 前不 fork -Z, --follow-context set SELinux context according to --target PID -h, --help 显示此帮助并退出 -V, --version 输出版本信息并退出 更多信息请参阅 nsenter(1)。 |
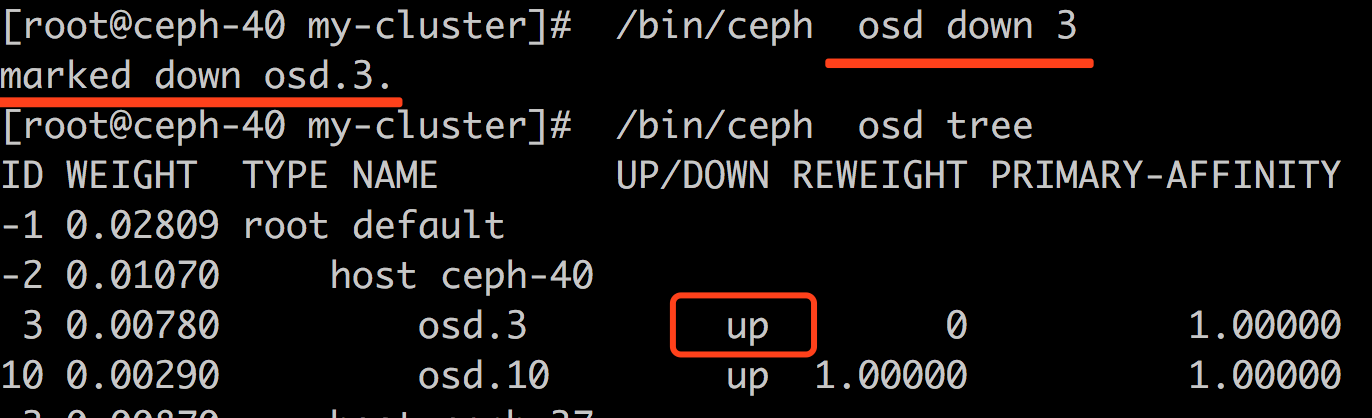
从 help 来看,只要使用了 -p 选项,就可以进入目标进程的pid名字空间,换言之,就可以只看到目标进程所在的名字空间的进程,用法如下:
|
1 |
nsenter -p -t $pid $cmd |
事实上,
|
1 |
nsenter -p -t 6806 top -n 1 |
看到的却是nsenter当前所在名字空间(严格来讲,这样描述也不太准确)的所有进程,为什么呢?
因为top参考的是 /proc 文件系统,所以,进入相应的mount空间也很重要,所以,正确的写法为:
|
1 |
nsenter -m -p -t 6806 top -n 1 |