|
1 |
setcap cap_net_raw,cap_net_admin=eip /usr/sbin/tcpdump |
golang 之静态链接
golang程序如果build时不是static的话,Linux上基本会依赖glibc的动态库的,通常也不是啥问题,但是,如果你期望一个更高版本的glibc,但是目标机器上没有,就尴尬了,这时候,其实可以编译成一个静态链接的二进制程序的,这时候需要的就是编译环境上有glibc-static,centos上的安装方法为:
|
1 |
yum install glibc-static -y |
那么,静态链接和动态链接后的目标文件差别会非常大吗?
- 从目标文件大小上来看,应该会大一些,但是并不大的离谱:
123# ll -h ./build/manager*-rwxr-xr-x 1 junjie20 staff 24M Feb 20 11:42 ./build/manager-rwxr-xr-x 1 junjie20 staff 28M Feb 20 11:57 ./build/manager-static - 或许这个差值基本比较固定,你的程序越大,这个差值的占比就越小;但是,和你使用到的glibc中的代码的多少有关系
- 从执行的角度来看,动态链接是会启动更快一些,也比较节省内存,因为底层的动态库在内存中只需要加载一次;但是,如果我们的程序是跑在容器中的,而且,通常容器中只有一个进程,那么,扩容器共享底层动态库的可能性就很小,因为它能不是同一个文件(或许有技术可以做到这一点)。
- 编译的时候,静态链接会比动态链接要慢一点点,应该差别也不会太明显
- 所以,过时的静态链接可能真的又可以回来了
静态链接只需要添加选项:
|
1 |
--ldflags '--extldflags "-static -fpic"' |
注意:
- 静态链接不代表完全没有依赖,有些情况下对内核版本是有要求的
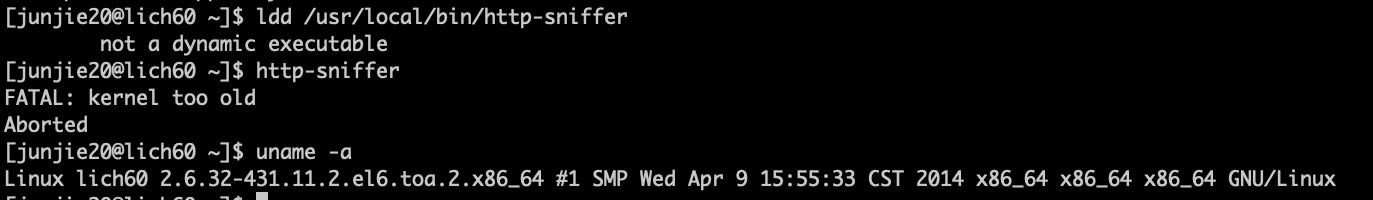
如何做Redis的持久化?
参考资料: http://tech.it168.com/a2012/0806/1381/000001381007_1.shtml
方式1: 简单的aof文件方式
这种方式只生成aof文件;
优点: 不会定期生成snapshot,对磁盘消耗小(不是少),也不会因为生成snapshot时写磁盘对服务带来影响(虽然影响不太大)
缺点: 重新启动服务时可能需要无法估计的时间
方式2: snapshot方式
该方式不生成aof文件,定期产生snapshot文件
优点: 重启服务时,启动速度快
缺点: 会丢失最后一次产生snapshot到意外宕机之间的写数据
方式3: aof + bgrewriteaof
1. 产生aof文件
2. 通过 bgrewriteaof 命令定期压缩aof(其实是根据内容中的数据重新生成aof)文件
优点: 不会导致aof文件太大而占用太大的磁盘文件,不会因为aof文件太大而导致重启服务时太慢
缺点: 毕竟重启服务还是要加载aof文件的
方式4: snapshot + aof + snapshot点 (该方式是否可行未经验证)
1. 定期产生snapshot文件
2. 产生snapshot文件后,删除文件中snapshot点之前的数据,这样aof就不会太大了
3. 服务重启时,先加载snapshop,在加载snapshot时间点后的aof文件
4. 这样的话,aof文件中记录的命令不应该有类似 incr decr之类的命令,应该都是set、delete之类的命令,这个和snapshot点的选择有关系(没法选择一个确切的snapshot点); 或者: snapshot期间允许用户执行写操作吗?不允许的话就没有这个问题了,如果不允许的话,这个条件也太苛刻了
5. 从redis的源码来看,是不会同时参考snapshot的rdb文件和aof文件的:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
/* Function called at startup to load RDB or AOF file in memory. */ void loadDataFromDisk(void) { long long start = ustime(); if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON) { if (loadAppendOnlyFile(server.aof_filename) == C_OK) serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"DB loaded from append only file: %.3f seconds",(float)(ustime()-start)/1000000); } else { rdbSaveInfo rsi = RDB_SAVE_INFO_INIT; errno = 0; /* Prevent a stale value from affecting error checking */ if (rdbLoad(server.rdb_filename,&rsi,RDBFLAGS_NONE) == C_OK) { serverLog(LL_NOTICE,"DB loaded from disk: %.3f seconds", (float)(ustime()-start)/1000000); /* Restore the replication ID / offset from the RDB file. */ if ((server.masterhost || (server.cluster_enabled && nodeIsSlave(server.cluster->myself))) && rsi.repl_id_is_set && rsi.repl_offset != -1 && /* Note that older implementations may save a repl_stream_db * of -1 inside the RDB file in a wrong way, see more * information in function rdbPopulateSaveInfo. */ rsi.repl_stream_db != -1) { memcpy(server.replid,rsi.repl_id,sizeof(server.replid)); server.master_repl_offset = rsi.repl_offset; /* If we are a slave, create a cached master from this * information, in order to allow partial resynchronizations * with masters. */ replicationCacheMasterUsingMyself(); selectDb(server.cached_master,rsi.repl_stream_db); } } else if (errno != ENOENT) { serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Fatal error loading the DB: %s. Exiting.",strerror(errno)); exit(1); } } } |
其实, redis4.0之后,是支持rdb+aof 方式的,这时候,loadAppendOnlyFile() 函数中有rdb相关逻辑,而且,这时候的aof文件的前面部分其实就是rdb文件的内容,但是依然叫做aof文件,所以,依然时候loadAppendOnlyFile() 函数就搞定了。
参考: Redis-4.0以后的混合持久化_gdlsky的博客-CSDN博客_redis混合持久化
关于snapshot的频率:
原来以为 save 300 10 解释为: 超过300s或者超过10条变更就snapshot,其实不是的,而是: 超过300s并且超过10条变更就snapshot
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
################################ SNAPSHOTTING ################################# # # Save the DB on disk: # # save <seconds> <changes> # # Will save the DB if both the given number of seconds and the given # number of write operations against the DB occurred. # # In the example below the behaviour will be to save: # after 900 sec (15 min) if at least 1 key changed # after 300 sec (5 min) if at least 10 keys changed # after 60 sec if at least 10000 keys changed # # Note: you can disable saving at all commenting all the "save" lines. # # It is also possible to remove all the previously configured save # points by adding a save directive with a single empty string argument # like in the following example: # # save "" save 900 1 save 300 10 save 60 10000 |
curl代理
默认情况下:
|
1 |
curl -x ip:port http://phpor.net/ |
使用的是普通代理,就是:
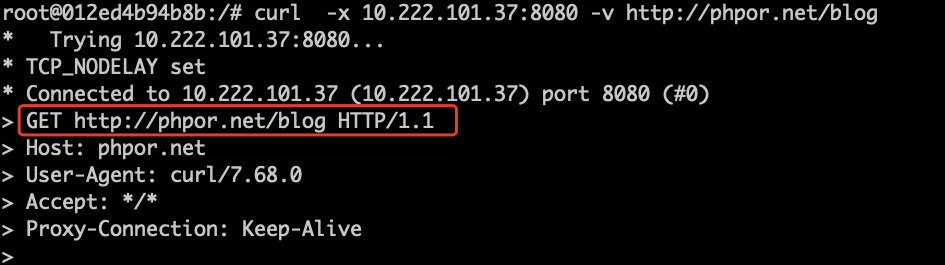
如果访问https地址,就是隧道代理:
|
1 |
curl -x ip:port https://phpor.net/ |
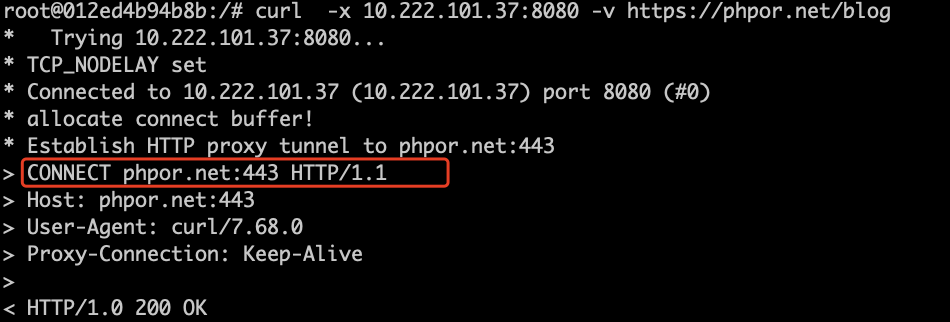
如果要让http请求也是用隧道代理,则添加 -p 选项:
|
1 |
curl -p -x 10.222.101.37:8080 -v http://phpor.net/blog |

如果要让https请求使用普通代理呢?没有找到这个选项
c++之typedef 和 typename
c中就有typedef 就是定义一个类型别名。
typename是c++中的,只是名字上和typedef相似,有时候还挨着用,就会感觉显得啰嗦。
typename用来告诉编译器后面这个东西是个名字空间或类中定义的类型,而不是成员变量
参考:
关于产品设计
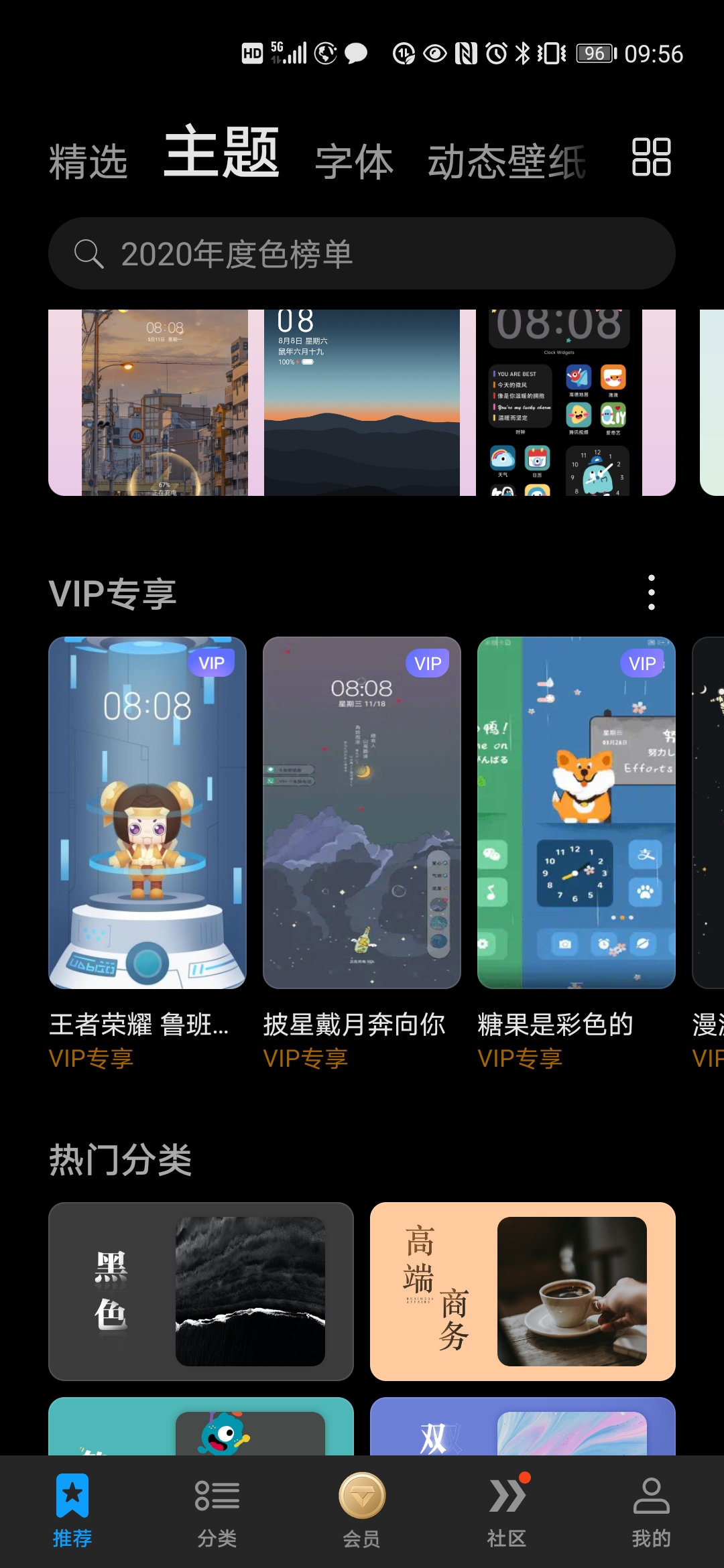
上面的VIP专享栏,每一项都注明了VIP专享,从技术角度来看,这个属于重复的元素,很不简洁,多余的东西就得去掉;但是,从产品设计的角度来讲,重复是为了强调,就是要通过视觉来刺激你,买VIP吧,买VIP吧,买V….
golang make map vs make slice
第二个参数的含义不同,make slice时,第二个参数是大小,make map时 ,第二个参数是容量。
流式解析http build query 字符串
脚本:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
#!/bin/env php <?php $filter = isset($argv[1])?$argv[1]:""; $arr = explode(".", $filter); while(!feof(STDIN)) { $line = trim(fgets(STDIN)); if (!$line) continue; $result = array(); parse_str($line, $result); $notFound = false; foreach($arr as $key) { if ($key == "") continue; if (!isset($result[$key])) { $notFound = true; break; } $result = $result[$key]; } if ($notFound) continue; if (is_array($result)) { print_r($result); echo "\n"; continue; } if (is_string($result)) { echo "$result\n"; } } |
受jq的启发
这个parser很奇怪, 处理的是 value 嵌套value的情况,生产上有这种情况,但是很少见。
tcp 的滑动窗口
tcp的滑动窗口是用来流控的,但是,如果一方不遵守,会怎样呢?如下:
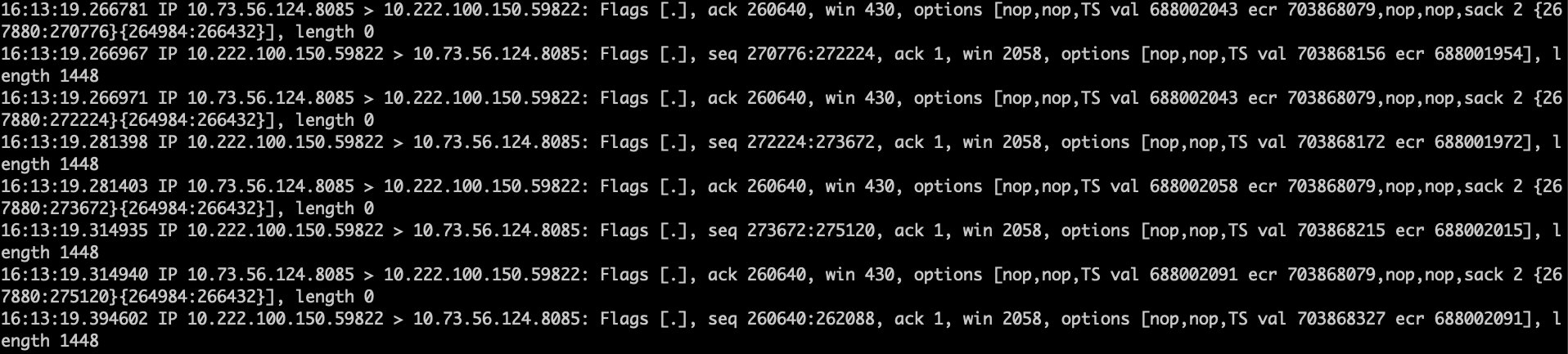
我们发现,虽然8085一直提示说win只有430,但是59822却完全无视,直接发送1448大小的数据; 8085也没有生气,也没有不ack,是不是很好玩。
好景不长,59822 觉得不好意思了,改发500大小的数据包了:

对于甲方来说,发送了一个小的win ,乙方未必按照小的win发送数据,只要甲方总能ack乙方发送的所有数据,乙方就可以总是发送一个很大的数据包;对于甲方来讲,其实可以通过不ack乙方,或者ack部分数据来制服乙方的。
最近在忙啥
自从雄飞提离职,我就开始了解lua版本的dmp,开始是性能优化,修补丢数据的情况,添加监控,分析指纹数据的流程,直到添加caid的支持。
最近这些事情不敢太随意,步步细心的去做,只是最近添加caid的事情,催的有些急,测试不到位,出了不少问题。
本来答应凯超那里做一些规则引擎的配置节目的事情,以及试金石的优化,都没时间做呢。
总结:
- 程序总是要有bug的,写完就上线,一定就出错,欲速则不达。
- 上完线不等于完事儿,必须多方面验证
- 尤其对数据的写操作,要有如果写错了的预案
- 有些时候,错误的认知会关上通往真理的大门,敢于否定自己,想办法来验证自己的想法,没有验证的结论就不一定对,就好比没有测试的程序就一定会出错一样